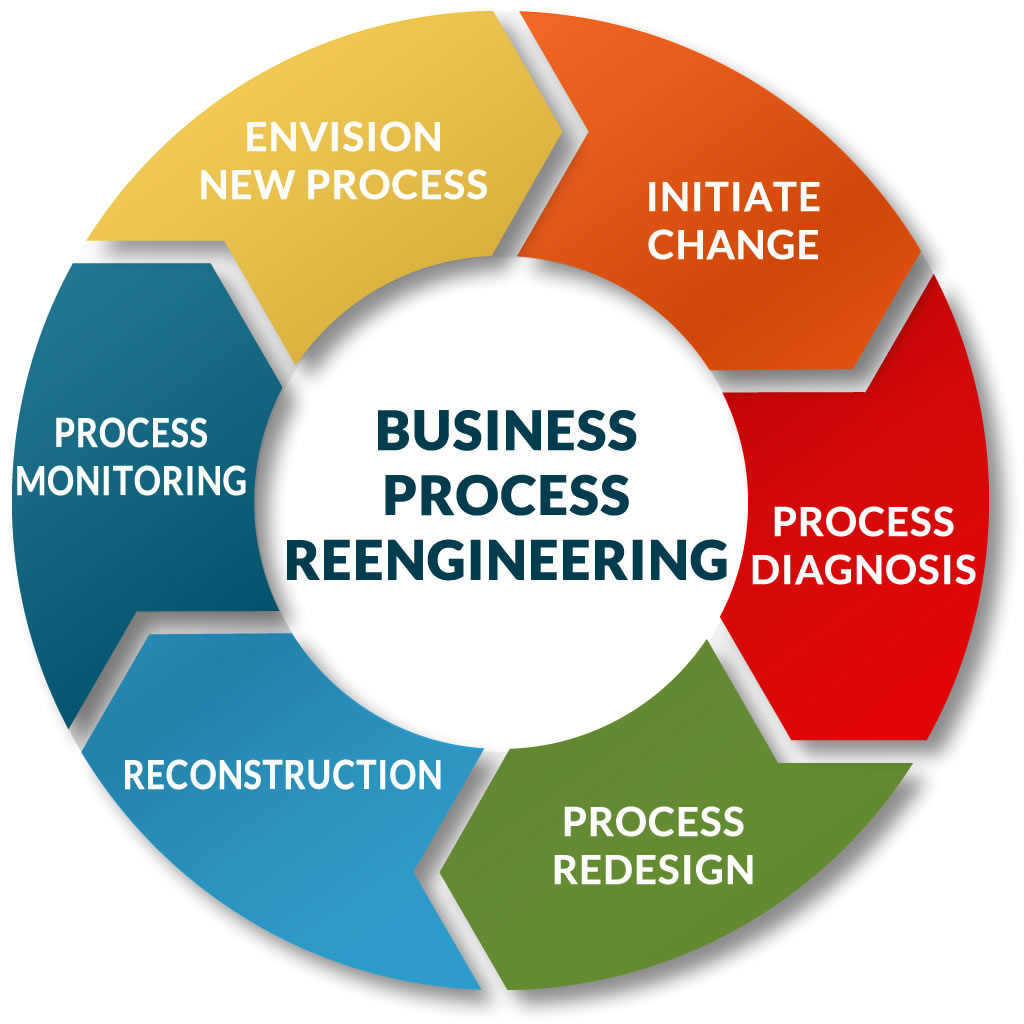
Business process reengineering
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is like giving your company a complete makeover. It’s not just about tweaking a few things here and there; it’s about fundamentally rethinking how you do business. Imagine you’re building a house. BPR is like tearing down the old blueprints and starting from scratch, considering new materials, technologies, and even a different architectural style.
Why BPR?
In today’s fast-paced, hyper-competitive world, businesses need to be agile and efficient. BPR aims to:
Increase Efficiency

By streamlining processes and eliminating unnecessary steps, companies can significantly reduce waste and increase productivity. Think of it as decluttering your workspace – it’s easier to find what you need and get things done faster.
Improve Customer Satisfaction
When processes are streamlined, customers experience faster service, fewer errors, and greater overall satisfaction. Happy customers mean repeat business and positive word-of-mouth.
Gain a Competitive Advantage
By rethinking how they operate, businesses can gain a significant edge over their competitors. BPR can lead to lower costs, higher quality products or services, and greater innovation.
Enhance Flexibility
In today’s dynamic business environment, companies need to be able to adapt quickly to changing market conditions. BPR can help organizations become more flexible and responsive to customer needs.
Boost Innovation
By challenging existing assumptions and exploring new ways of doing things, BPR can foster a culture of innovation within an organization.
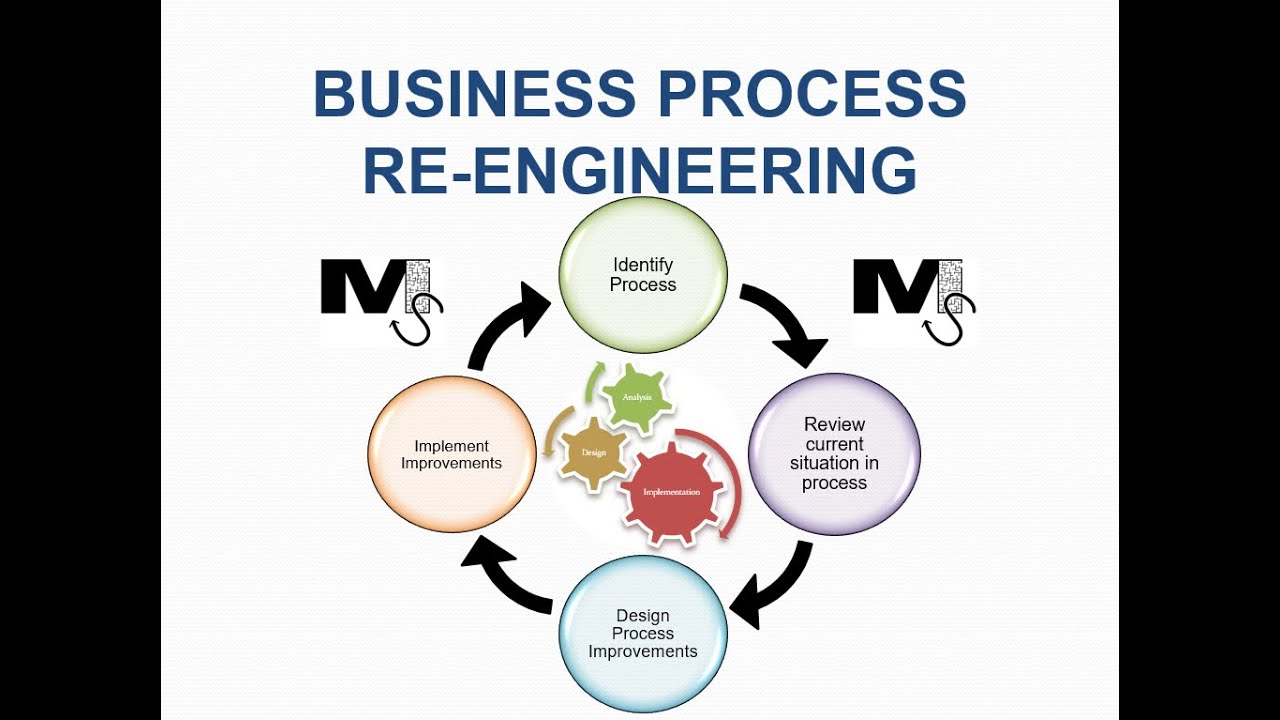
The BPR Process
BPR is not a quick fix. It’s a comprehensive and often challenging undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a general overview of the BPR process:
Define Scope and Objectives
The first step is to clearly define the scope of the reengineering project. What processes will be included? What are the specific goals of the project? For example, are you aiming to reduce costs, improve customer service, or increase market share?
Analyze Existing Processes
Once the scope is defined, it’s crucial to thoroughly analyze the current processes. This involves mapping out the steps involved, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, and understanding the “as-is” state of the business.
Identify Key Business Processes
Not all processes are created equal. Focus on the core business processes that have the greatest impact on the company’s performance and customer satisfaction.
Develop New Processes
This is the heart of the BPR process. Based on the analysis of existing processes and the desired outcomes, new, more efficient and effective processes are designed. This often involves challenging traditional assumptions and exploring innovative solutions.
Implement and Monitor
Once the new processes are designed, they need to be implemented across the organization. This may require changes to technology, training, and organizational structure.
Continuous Improvement
BPR is an ongoing process. After implementation, it’s essential to continuously monitor the performance of the new processes and make adjustments as needed.
Key Principles of BPR
Several key principles guide the BPR process:
Focus on Customers
The primary focus of BPR should be on meeting the needs and expectations of customers.
Rethink Fundamental Processes
BPR is about radical change, not incremental improvement. It requires a fundamental rethinking of how work is done.
Organize Around Outcomes, Not Tasks
Instead of focusing on individual tasks, BPR emphasizes achieving desired outcomes.
Integrate Information Flow
BPR seeks to break down departmental silos and integrate information flow across the organization.
Empower Employees
BPR requires the active participation and engagement of employees at all levels.
Tools and Technologies
A variety of tools and technologies can be used to support the BPR process, including:
Business Process Modeling
Software tools can be used to map and analyze existing processes, simulate new processes, and identify potential bottlenecks.
Data Analytics
Data analytics can be used to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement within existing processes.
Automation
Automation technologies, such as robotic process automation (RPA), can be used to automate repetitive tasks and free up employees for more strategic work.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can provide the flexibility and scalability needed to support new, more agile business processes.
Challenges of BPR
BPR is not without its challenges:
Resistance to Change
One of the biggest challenges of BPR is overcoming resistance to change from employees, managers, and other stakeholders.
High Costs
BPR can be a costly undertaking, requiring significant investments in technology, training, and consulting services.
Disruption to Operations
Implementing new processes can disrupt normal business operations, leading to temporary inefficiencies and potential customer dissatisfaction.
Difficulty in Measurement
It can be difficult to accurately measure the results of BPR and demonstrate a clear return on investment.
Success Factors of BPR
The success of a BPR project depends on several key factors:
Strong Leadership
Strong leadership is essential to drive the BPR process and overcome resistance to change.
Employee Involvement
Engaging employees at all levels in the BPR process is crucial for successful implementation.