:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/inventory-management-8595e839c2884128997ca77f00a8da2b.jpg)
Inventory management
Inventory management might sound like a dry topic, but it’s the backbone of any successful business, especially if you’re dealing with physical products. Think of it like this: your inventory is your lifeblood. It’s what you use to fulfill orders, generate revenue, and keep your customers happy.
But managing inventory can be a real headache. You’ve got to keep track of what you have, where it is, and how much it’s costing you. You need to make sure you have enough stock to meet demand, but not so much that you’re wasting money on storage and risking spoilage.
Don’t worry, though! This guide will break down inventory management in a relaxed, easy-to-understand way. We’ll cover the basics, explore some key strategies, and even touch on some cool inventory management tools that can make your life easier.
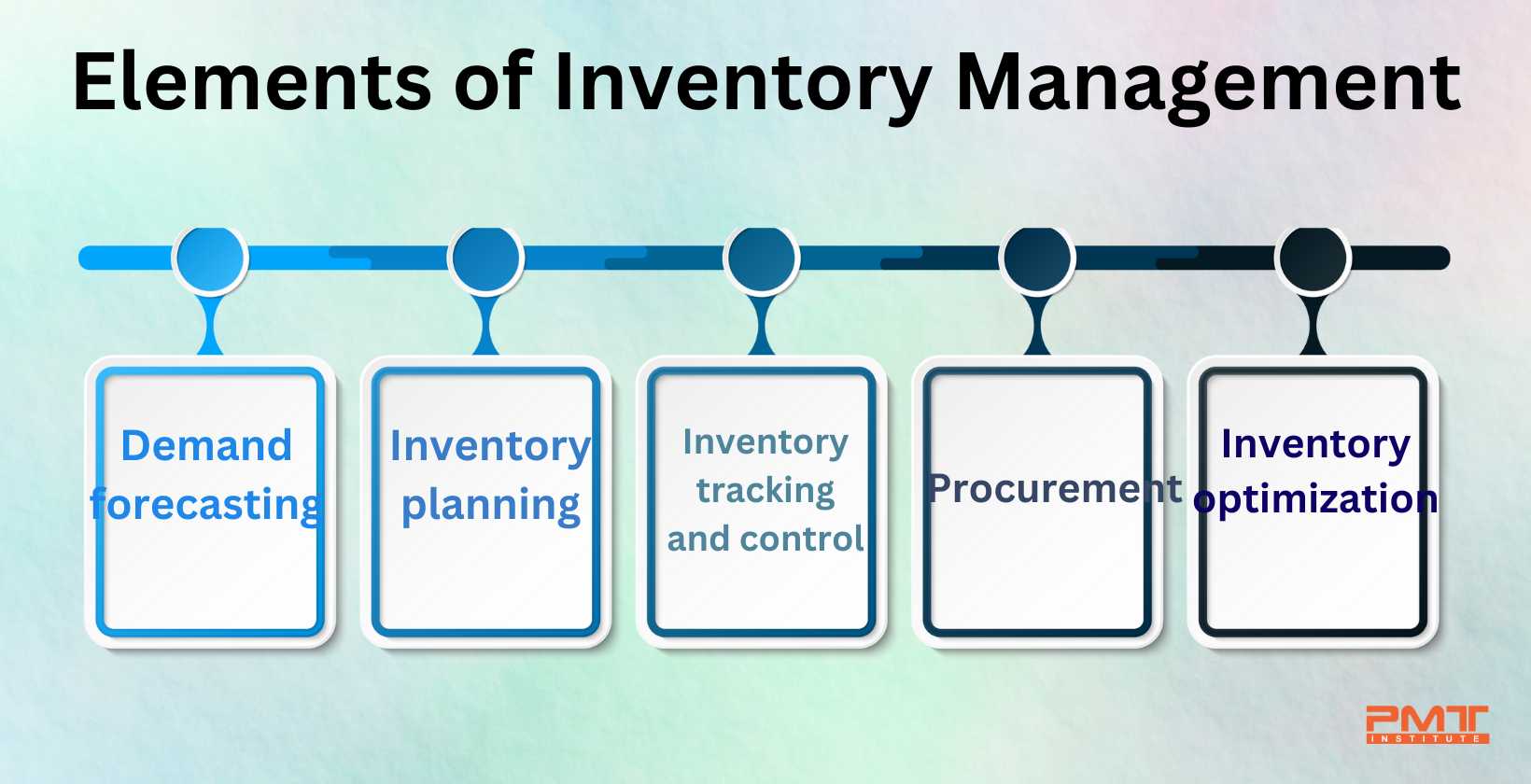
What is Inventory Management?
Simply put, inventory management is the process of overseeing the flow of goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption. It involves a whole bunch of activities, including:
1. Planning and Forecasting
Demand forecasting: Predicting how much of each product you’ll need to meet customer demand. This involves analyzing past sales data, considering seasonal trends, and keeping an eye on market conditions.
2. Purchasing and Procurement

Sourcing and selecting suppliers: Finding reliable and cost-effective suppliers for your products.
3. Storage and Warehousing
Warehouse management: Effectively organizing and storing your inventory in a way that maximizes space utilization and minimizes handling costs.
4. Inventory Control
Cycle counting: Regularly checking inventory levels to ensure they match your records.
Why is Inventory Management Important?
Effective inventory management is crucial for the success of any business, especially in today’s competitive landscape. Here are a few key reasons why:
Increased profitability: By minimizing stockouts and reducing holding costs, you can improve your bottom line.
Key Inventory Management Strategies
Here are some strategies that can help you improve your inventory management:
1. Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory
This strategy aims to minimize inventory levels by ordering and receiving goods only when they are needed.
2. Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
This model helps determine the optimal order quantity to minimize the total cost of inventory, which includes ordering costs and holding costs.
3. Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
In this model, the supplier is responsible for managing the inventory levels at the customer’s location.
Inventory Management Tools
There are many tools available to help you manage your inventory more effectively. Here are a few examples:
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): These software applications help you track inventory movements, optimize warehouse space, and improve order fulfillment.
Conclusion
Inventory management is a critical function for any business that deals with physical products. By implementing effective inventory management strategies and utilizing the right tools, you can improve profitability, enhance customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive advantage.
Remember that inventory management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. By regularly reviewing your inventory levels, analyzing your performance, and adapting your strategies as needed, you can ensure that your inventory is always working for you, not against you.