Performance benchmarking
Performance benchmarking is a critical process for any organization, regardless of size or industry. It involves comparing your organization’s performance against established standards or the performance of other organizations. Think of it like this: imagine you’re running a race. Benchmarking helps you understand how fast you’re running compared to other runners, where you can improve your speed and technique, and ultimately, how to win the race.
In the business world, “winning the race” translates to achieving superior performance, gaining a competitive advantage, and ultimately, increasing profitability. Benchmarking provides valuable insights into areas where your organization excels and areas where improvement is needed.
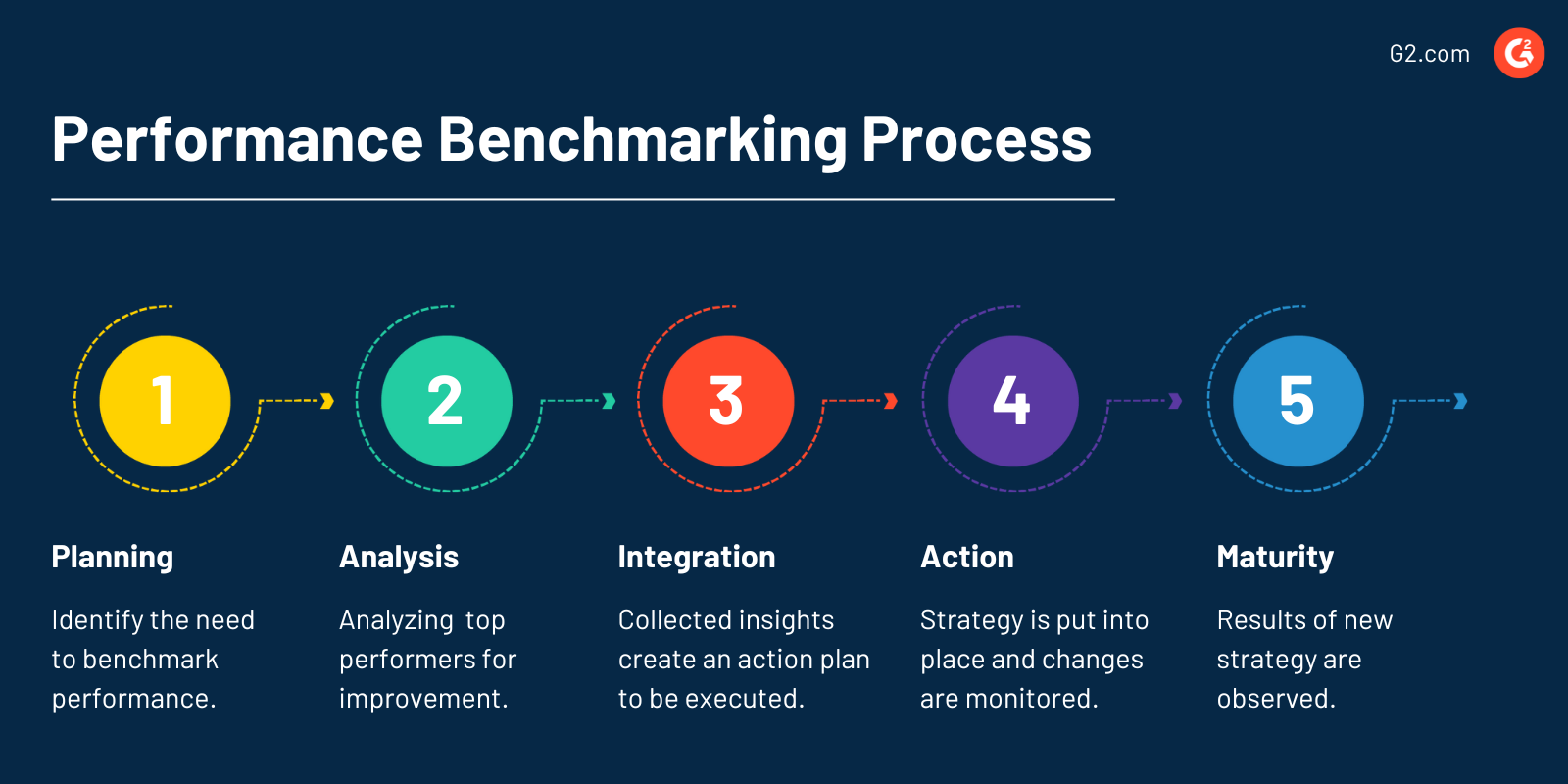
Here’s a breakdown of performance benchmarking in a relaxed and easy-to-understand manner:
1. Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)

Before you can start comparing, you need to determine what exactly you’re measuring. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are the crucial metrics that reflect your organization’s success.
Examples of KPIs:
Financial KPIs: Revenue growth, profitability margins, return on investment (ROI), cost per acquisition (CPA)
2. Choosing Benchmarking Partners
Who are you comparing yourself to? There are several benchmarking options:
Internal benchmarking: Comparing different departments or divisions within your own organization.
3. Collecting and Analyzing Data
Once you’ve identified your KPIs and chosen your benchmarking partners, it’s time to gather data. This may involve:
Surveys and questionnaires: Collecting data from employees, customers, and suppliers.
Data analysis is crucial. You need to identify trends, compare your performance to your benchmarks, and pinpoint areas for improvement.
4. Identifying Areas for Improvement
Benchmarking should not just be about identifying weaknesses. It’s equally important to identify areas where your organization excels. This allows you to:
Replicate successful practices: Share best practices across departments or divisions.
5. Implementing Change and Continuous Improvement
The final step is to implement the necessary changes to improve performance. This may involve:
Process improvement initiatives: Streamlining processes, eliminating waste, and improving efficiency.
Benefits of Performance Benchmarking
Improved performance: By identifying areas for improvement and implementing changes, you can significantly boost your organization’s performance.
Common Challenges in Performance Benchmarking
Data collection and analysis: Gathering accurate and reliable data can be challenging and time-consuming.
Conclusion
Performance benchmarking is an ongoing process that requires continuous effort and commitment. By regularly assessing your performance against established standards or the performance of other organizations, you can gain valuable insights into areas for improvement, enhance your competitiveness, and drive organizational success.
Remember, benchmarking is not just about identifying weaknesses; it’s also about identifying strengths and leveraging them to your advantage. By embracing a culture of continuous improvement and using benchmarking as a tool for growth and development, your organization can achieve its full potential.