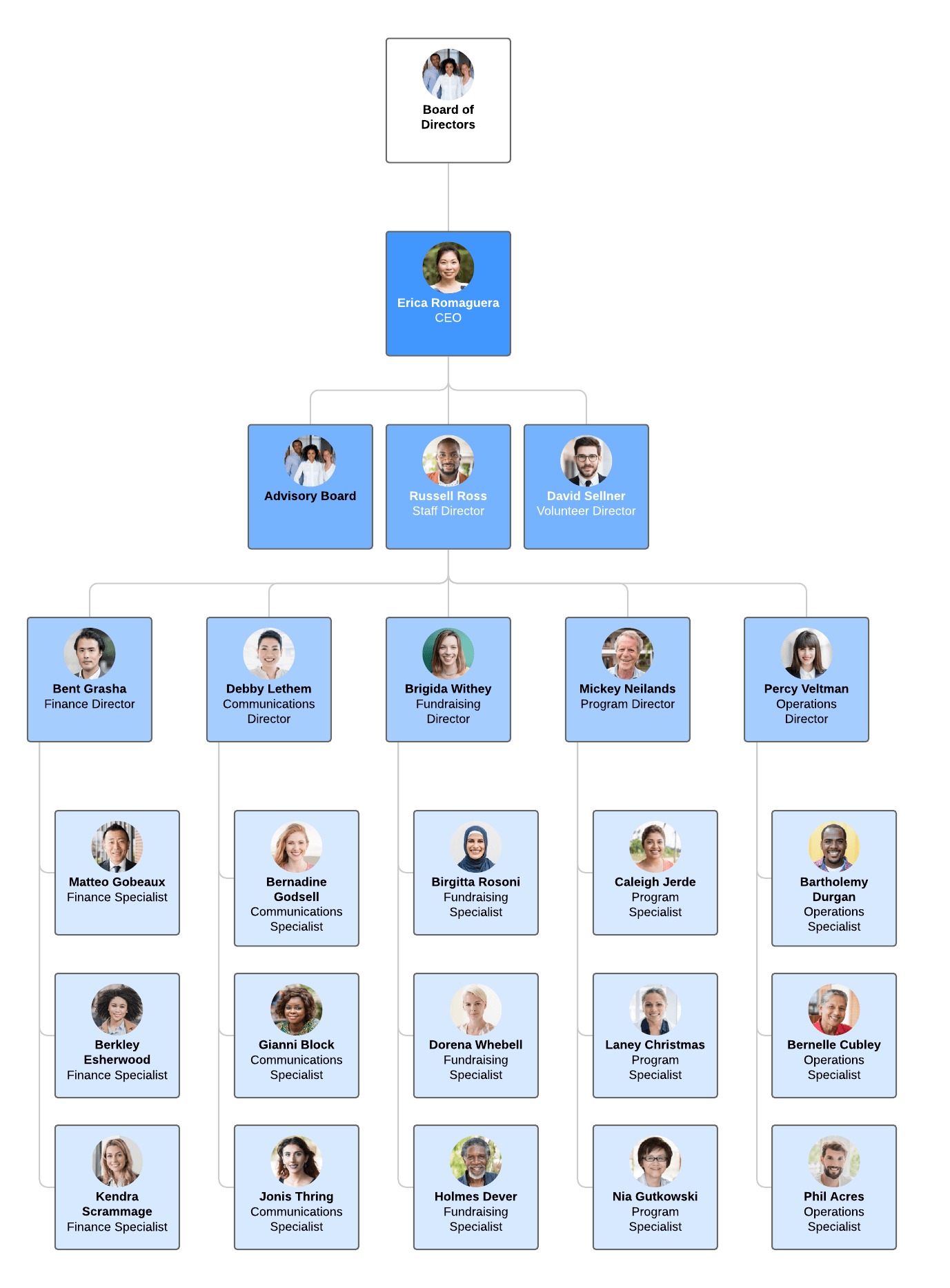
Organizational structure
Unlocking Organizational Structure: A Relaxed Guide
So, you’re curious about how companies are set up? You’ve probably heard terms like “hierarchy,” “teamwork,” and “flat structure” thrown around. But what do they really mean? Let’s break down organizational structure in a way that’s easy to understand.
1. The Big Picture: What is Organizational Structure?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/organizationalstructure-final-5d4f333cdb174faea796402175ff305b.png)
Think of organizational structure as the blueprint for a company. It’s how roles, responsibilities, and relationships are defined within the organization. It determines who reports to whom, how decisions are made, and how information flows.
2. Common Types of Organizational Structures
Hierarchical Structure
This is the classic “top-down” model. Imagine a pyramid:
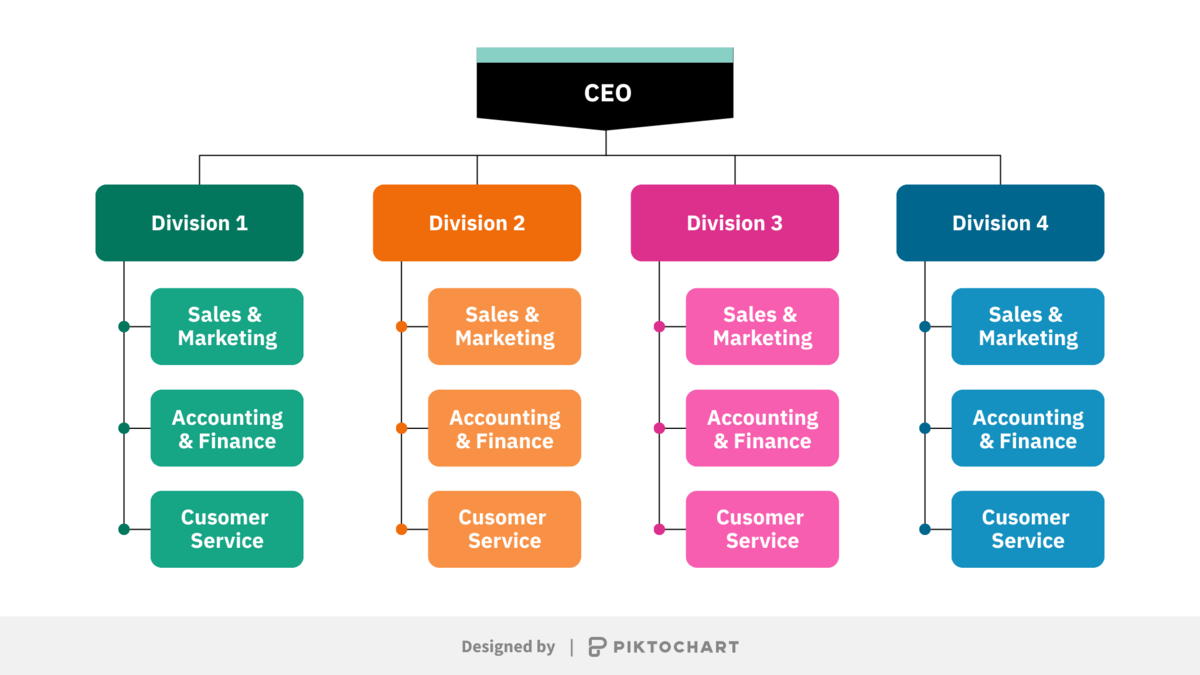
The Top: You have the CEO at the very top, with ultimate authority.
Pros:
Clear lines of authority: Everyone knows who their boss is.
Cons:
Can stifle creativity and innovation: Employees may feel micromanaged and hesitant to take risks.
Matrix Structure
This structure is more complex. Employees report to two managers:
Functional Manager: Responsible for their specific skills or department (e.g., marketing manager, engineering manager).
Pros:
Enhanced communication and collaboration: Employees with diverse skills work together on projects.
Cons:
Potential for conflict: Employees may have conflicting priorities from their functional and project managers.
Flatarchy (Flat Structure)
This structure emphasizes teamwork and decentralization:
Fewer layers of management: There are minimal levels between top management and employees.
Pros:
Increased employee motivation and engagement: Employees feel valued and empowered.
Cons:
Can lead to confusion and lack of direction: Clear lines of authority may be less defined.
3. Factors that Influence Organizational Structure
Several factors influence the type of organizational structure a company chooses:
Company size: Small startups may have a flat structure, while large corporations may have a hierarchical one.
4. The Importance of Organizational Structure
Organizational structure is crucial for a company’s success:
Improved efficiency and productivity: A well-defined structure can streamline workflows and minimize bottlenecks.
5. Choosing the Right Organizational Structure
There is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to organizational structure. The best structure for a particular company will depend on its specific needs and circumstances.
Key Considerations:
What are the company’s goals and objectives?
6. Organizational Structure and the Future of Work
The traditional hierarchical structure is increasingly being challenged in today’s rapidly changing world.
Rise of remote work: The rise of remote work is blurring traditional lines of authority and creating new challenges for organizational design.
Conclusion
Organizational structure is a complex topic, but it’s essential for any company that wants to be successful. By understanding the different types of structures and the factors that influence them, companies can choose the best structure to meet their unique needs and achieve their goals. In today’s dynamic world, organizations must be agile and adaptable, and the right organizational structure can play a crucial role in enabling this agility.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered professional advice.
I hope this article provides a helpful overview of organizational structure!